A multi-institution research team led by the University of Pittsburgh secured a $22 million grant from the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) to develop a device combining artificial intelligence, bioelectronics and regenerative medicine to regrow muscle tissue, especially after combat injuries.
McGowan Institute for Regenerative Medicine affiliated faculty members involved in this effort include:
- Stephen Badylak, DVM, PhD, MD, professor of surgery at Pitt and deputy director of the McGowan Institute for Regenerative Medicine (principal investigator)
- Yoram Vodovotz, PhD, professor in the Department of Surgery, University of Pittsburgh, and director of the Center for Inflammation and Regeneration Modeling at the McGowan Institute
- Ruben Zamora, PhD, research professor in the Department of Surgery, University of Pittsburgh
- Douglas Weber, PhD, associate professor in the Department of Bioengineering, University of Pittsburgh
- Bryan Brown, PhD, associate professor in the Department of Bioengineering, University of Pittsburgh
- Tzahi Cohen-Karni, PhD, assistant professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering at Carnegie Mellon University
- Adam Feinberg, PhD, professor in the Departments of Biomedical Engineering and Materials Science and Engineering at Carnegie Mellon University
Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University, Northwestern University, Rice University, University of Vermont, University of Wisconsin and Walter Reed National Military Medical Center also are part of this four-year initiative.
When more than 20% of a muscle is damaged, as is common for soldiers wounded in recent overseas conflicts, the tissue can’t regenerate and a stiff scar forms in place of the missing muscle, which often leads to significant disability.
“With these severe injuries it’s been drilled into us through all of our training that functional muscle replacement is not possible,” said principal investigator Dr. Badylak. “The sort of technology we’re developing offers hope where there otherwise would have been no hope.”
Dr. Badylak envisions creating a device that would change the environment inside larger wounds to help them heal the way smaller wounds do naturally.
Smaller, self-healing wounds typically switch from inflammatory to anti-inflammatory conditions a couple weeks after the initial injury. Dr. Badylak imagines kicking larger wounds into anti-inflammatory mode as early as day three or four, and then again a few days later, repeating the cycle until the muscle rebuilds itself, similar to the way fetal wounds heal without forming a scar.
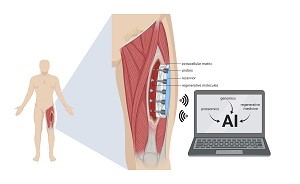
All of that would be accomplished by a smart device implanted inside the wound.
The device will monitor key molecular signals at each stage of healing — from the first hours after injury to the days and weeks that follow — and deliver specific molecules at specific times under the direction of artificial intelligence.
The first two years of the project will involve developing the device, then the next two years will involve close collaboration with surgeons at Walter Reed, who treat patients with major muscle loss, to refine the design so that it’s suitable for the clinic.
Meanwhile, the researchers will be working with industry partners and the U.S. Food & Drug Administration to identify and clear regulatory hurdles that might slow down clinical translation. For instance, it’s possible to test whether the components of the device are safe to use in the human body while the overall design is evolving.
“We’re developing the science and the device in mostly an academic setting,” Dr. Badylak said. “If that’s done without consideration of regulatory and industry requirements, patients would never see it because it would remain buried in institutions with no clear path for clinical translation.”
One of the companies engaging in this process is ECM Therapeutics, which Dr. Badylak spun out of Pitt in 2018 to speed up the clinical translation of several extracellular matrix technologies developed by his lab. Dr. Badylak and Pitt both have a financial stake in the company.
Additional investigators on the grant include Paul Cohen, PhD, and Milos Hauskrecht, PhD, of Pitt; Jonathan Rivnay, PhD, of Northwestern University; Jacob Robinson, PhD, Ashok Veeraraghavan, PhD, and Omid Veiseh, PhD, of Rice University; Gary An, MD, and Robert Chase Cockrell, PhD, of the University of Vermont; Peng Jiang, PhD, of the University of Wisconsin; and Eric Elster, MD, and Seth Schobel, PhD, of Walter Reed.
Illustration: “Smart” Wound-Healing Device: The device will go onto injured muscle to deliver and measure molecules in real time, under the guidance of artificial intelligence. UPMC.
Read more…
UPMC/PittHealthSciences News Release
University of Pittsburgh Swanson School of Engineering News Release
