Combining ultrasound energy and microbubbles to poke holes in cells may prove to be a new tool in the fight against cardiovascular disease and cancer, according to researchers from the University of Pittsburgh and UPMC. A study on this gene therapy approach, called sonoporation, appears in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). McGowan Institute for Regenerative Medicine affiliated faculty members Flordeliza Villanueva, MD, Professor of Medicine in the Division of Cardiology and Vice Chair for Pre-Clinical Research of the Department of Medicine, and Simon Watkins, PhD, Founder and Director of the Center for Biologic Imaging at the University of Pittsburgh, member of the Pittsburgh Cancer Institute, and also a Professor and Vice Chairman within the Department of Cell Biology, are co-authors on the study.
“We can use ultrasound energy in combination with small, gas-filled bubbles to selectively open up cells to allow the delivery of therapeutic agents,” said Brandon Helfield, PhD, lead author of the study and a postdoctoral fellow at the Center for Ultrasound Molecular Imaging and Therapeutics at UPMC. “With a focused ultrasound beam, this approach lets us tune this delivery to the precise location of disease while sparing healthy tissue. Our study looks at some of the biophysics at play and helps us get closer to refining this technique as a clinical tool.”
Current approaches to gene therapy often use viruses to gain access inside cells, which can cause severe side-effects, including inflammatory immune system reactions. To address this, researchers have developed gene-loaded intravascular microbubbles that can be targeted to release their payloads by direct navigation of focused ultrasound energy.
The Pitt researchers developed an ultrafast imaging camera capable of reaching speeds up to 25 million frames per second—the only one of its kind in North America. Using the camera, these researchers examined the biophysics of sonoporation. They determined that the oscillating bubbles need to generate a minimum amount of localized shear stress, beyond which cell membranes perforate and allow entry of a targeted therapeutic.
“By allowing us to actually see the microbubbles vibrating at millions of times per second, our unique camera enabled us to determine that microbubble-induced shear stress is the critical factor for sonoporation,” said Xucai Chen, PhD, research associate professor of medicine, Pitt Division of Cardiology, and Pittsburgh Heart, Lung and Blood Vascular Medicine Institute, who co-developed the camera system. “This new information, in turn, will facilitate the intelligent design of treatment protocols and microbubble fabrication to preferentially cause the desired effect of opening nearby cells. It also gives us a starting point to investigate how cells cope with this treatment.”
Researchers believe the findings will help them understand how the process of sonoporation works, as well as how experts can tailor the approach, including ultrasound amplitude levels and microbubble designs, toward its eventual clinical use.
“It’s critical for us to understand the biophysical mechanisms of sonoporation in order to translate this approach into an effective gene or drug delivery tool for patients,” said Dr. Villanueva, the senior author of the investigation. “Building on the PNAS study, we are continuing to investigate how sonoporation affects the function of treated cells and to develop strategies to maximize its therapeutic effects.”
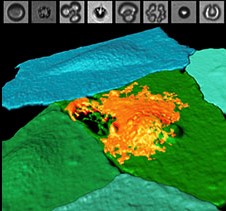
Illustration: Fluorescently labeled endothelial cell monolayer, pseudocolorized in blue/green, and imaged using spectral confocal microscopy. One cell has been selectively perforated via ultrasound-induced microbubble cavitation (simultaneously captured by ultrafast imaging, top panels), allowing the entrance of a model therapeutic (orange). UPMC.
Read more…
UPMC/University of Pittsburgh Schools of the Health Sciences Media Relations News Release
Abstract (Biophysical insight into mechanisms of sonoporation. Brandon Helfield, Xucai Chen, Simon C. Watkins, and Flordeliza S. Villanueva. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences; August 22, 2016.)
